The concept of microgrids has been around for a while. However, it’s only recently gained popularity as more and more communities look for ways to generate their own electricity and reduce their dependence on the utility grid. But what exactly is a microgrid, and how does it work? Below, we will break down the basics of microgrids into three key points that even a 4th grader can understand.
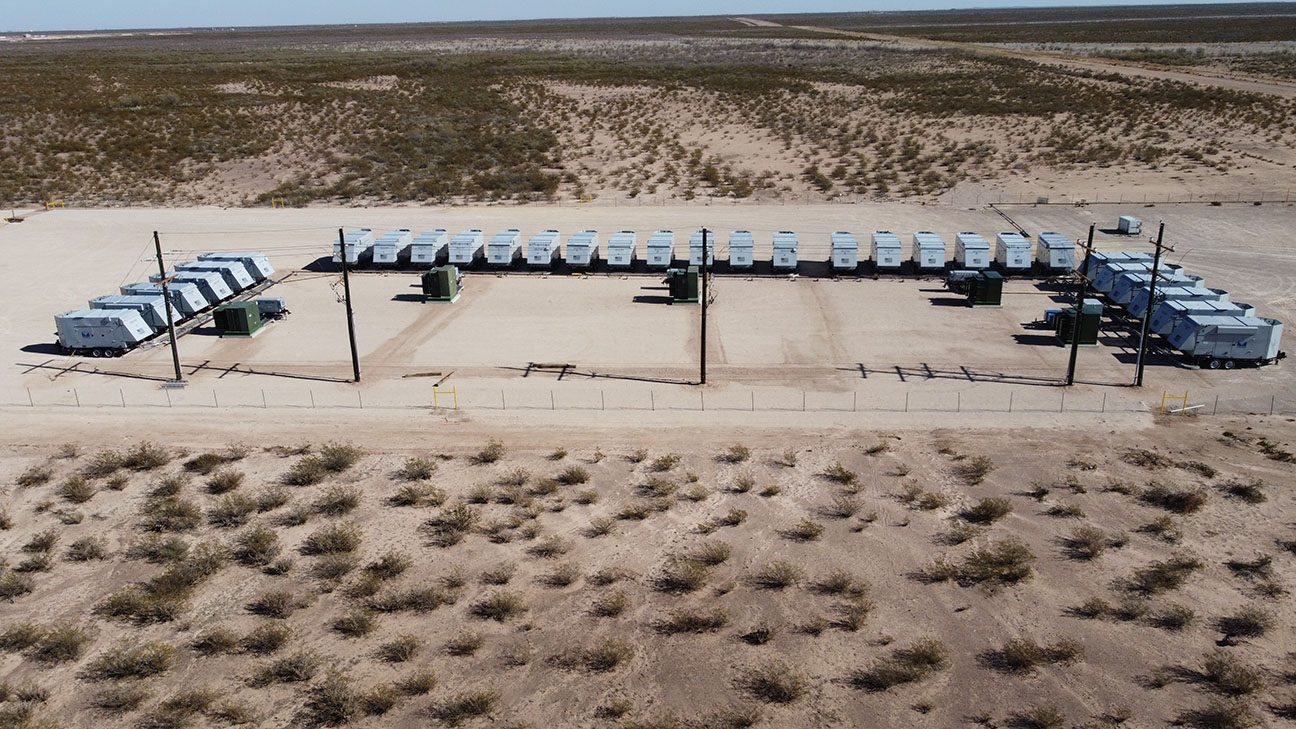
First, a microgrid is a small-scale power system that can operate by itself or with the main power grid. A microgrid can generate its own electricity. It can do this using sources like generators or renewable sources like solar panels or wind turbines. It can also draw power from the main utility grid. However, the key difference is that a microgrid can also store energy in batteries or other energy storage systems, allowing it to operate even when the utility grid is down. It’s good to have a variety of power sources in a microgrid so that when one or more of them are unavailable, you will still have power. For example, if the sun isn’t shining, you may not be able to use solar power. It might be good to have a generator as part of the microgrid to make it more reliable.
What are some benefits of microgrids?
Second, microgrids are becoming increasingly popular because they offer a range of benefits to communities and businesses. One of the main advantages of a microgrid is that it provides greater energy security and resiliency. This can be very helpful to areas prone to power outages caused by extreme weather events or other emergencies. In addition, microgrids can help reduce energy costs by allowing businesses and communities to generate their own power, enabling the user to peak shave*, lower demand charges, and in some cases sell excess energy back to the grid. Microgrids can also help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by using renewable energy sources or lower-emission sources, such as natural gas, to improve overall energy efficiency.
*Peak shaving is managing the amount of electricity that is used during high-demand periods by moving your electricity usage to a different time of day than most companies. Some utilities charge extra for high-demand periods.
What about installing and maintaining a microgrid?
Third, microgrids are relatively easy to install and maintain. This makes them a practical solution for a wide range of applications. While the cost of installing a microgrid can vary depending on the size and complexity of the system, advances in technology have made it more affordable for businesses and communities to install their own microgrids. For example, installing a 1MW microgrid would cost much less when compared to the cost of upgrading the utility infrastructure such as transmission, distribution, substations, or power plants to provide an additional 1MW of load capacity. Moreover, microgrids can be customized to meet the specific needs of a particular community or business, whether that means generating more power or maximizing energy efficiency.
In conclusion, microgrids are a versatile and practical solution for businesses and communities looking to generate their own power and increase energy security. They offer a range of benefits, from improved resiliency to reduced energy costs and emissions, and can be customized to meet specific needs. With the continued development of technology and the growing demand for renewable energy sources, it seems likely that microgrids will become an increasingly common sight in communities across the world.
Do you want to know more about how Mesa Solutions can help you achieve your microgrid goals? Click the button below to request more information.












