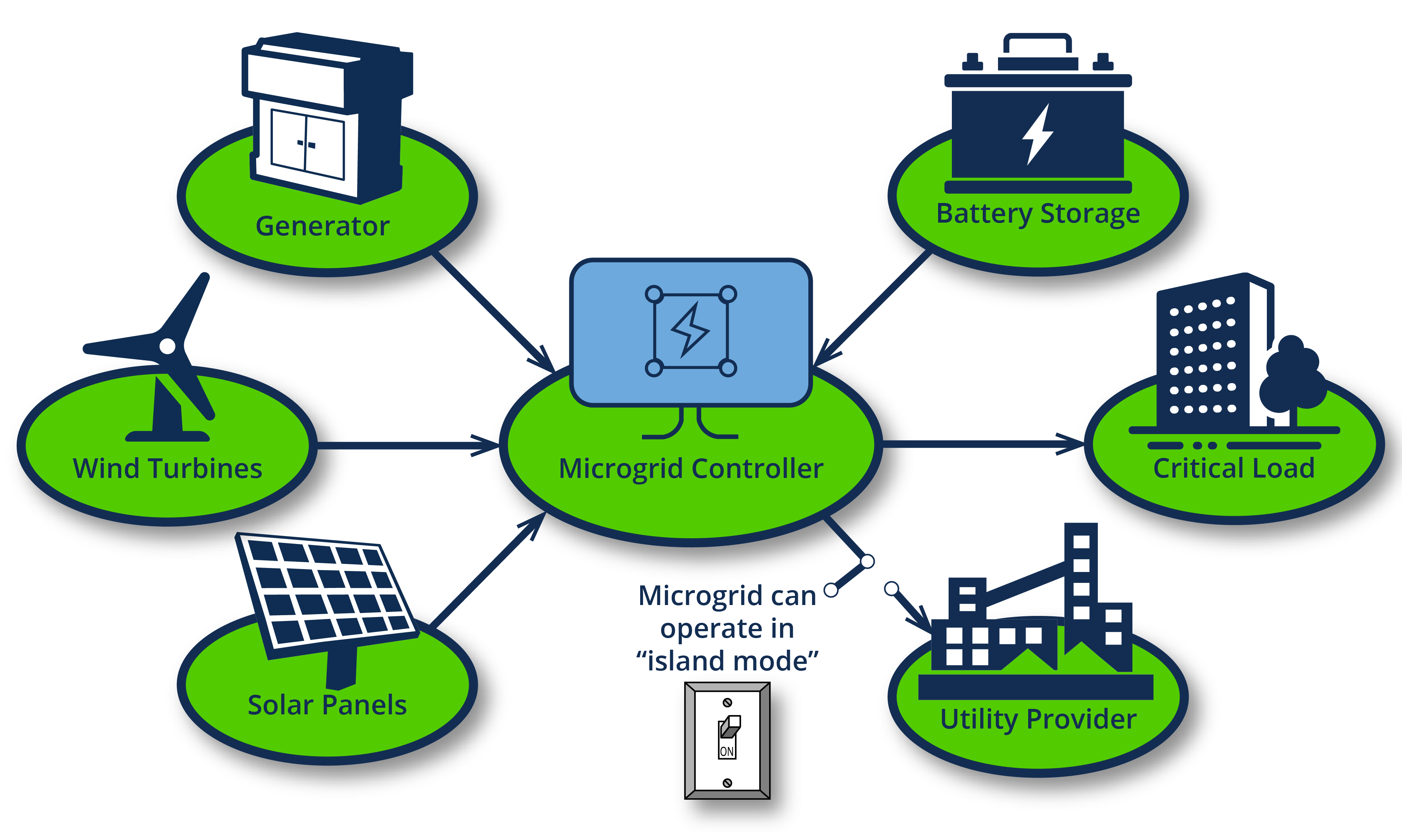
As interest in power reliability and renewable energy management continues to grow, the subject of “microgrids” continues to gain consideration. It’s also important to understand how microgrid controllers play a role in this space.
Microgrids are decentralized power systems that consist of distributed energy resources (DERs) such as renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and conventional generators. Microgrid controllers are systems that enable the effective coordination of microgrid components such as renewable energy sources, energy storage systems, and loads. Microgrid controllers play an important role in managing the distribution of energy within a microgrid by ensuring optimal use of available resources, minimizing energy losses, and reducing operating costs. Below, we will explore the functions of microgrid controllers and the benefits they offer.
Functions of Microgrid Controllers
Microgrid controllers are designed to enable effective coordination of microgrid components, and they do this by performing several functions.
One of the primary functions of a microgrid controller is to manage the distribution of energy within the microgrid. The controller ensures that the available energy resources are used optimally and that energy losses are minimized. To achieve this, the controller continuously monitors the available energy resources and their utilization and adjusts the distribution of energy accordingly. The controller also manages the charging and discharging of energy systems, ensuring that they are utilized optimally.
Another function of a microgrid controller is to manage the interaction between the microgrid and the main power grid. The controller is responsible for managing the transfer of energy between the microgrid and the main grid, ensuring that the microgrid operates within the specified operating limits. In the event of a power outage or any other form of disruption to the main grid, the microgrid controller can seamlessly switch the microgrid to islanded mode, ensuring that the microgrid can operate independently.
Microgrid Controller Benefits
The benefits of microgrid controllers are numerous.
One of the main benefits of microgrid controllers is improved energy efficiency. The controller ensures that the available energy resources are used optimally, minimizing energy losses, and reducing operating costs. The controller also ensures that renewable energy sources are utilized to their maximum potential, reducing the dependence on fossil fuels, and lowering the carbon footprint.
Another benefit of microgrid controllers is improved grid stability and reliability. The controller ensures that the microgrid operates within the specified operating limits, and in the event of a deviation, takes corrective measures to ensure that the microgrid remains stable. This reduces the likelihood of power outages and ensures that the microgrid can operate independently in the event of a disruption to the main grid. In this way, microgrids can also strengthen the resilience of the utility grid.
Lastly, microgrid controllers can reduce the costs of microgrids by reducing the reliance on the main grid and minimizing the operational costs of the DERs. By optimizing the operation of the DERs within the microgrid, the microgrid controllers can reduce the need for purchasing power from the main grid, thus reducing energy bills. Additionally, the microgrid controllers can manage the operation of the DERs to minimize the operation costs. For instance, microgrid controllers can charge the energy storage systems during periods of low energy prices and discharge the energy storage systems during periods of high energy prices, thus reducing the overall energy costs.
In conclusion, microgrid controllers play a critical role in the management of microgrids. They ensure effective coordination of microgrid components, manage the distribution of energy within the microgrid, and ensure the stability and reliability of the microgrid. The benefits of microgrid controllers include improved energy efficiency, grid stability, reliability, and reduced operating costs. As the use of microgrids continues to grow, the importance of microgrid controllers will continue to increase.